Windows Server 2025 – Part 4 (Services Removed or no longer developed)
Services Removed in Windows Server 2025
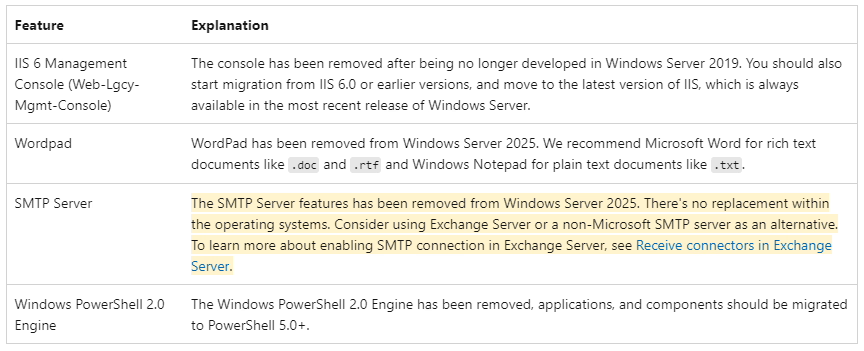
Feature: IIS 6 Management Console (Web-Lgcy-Mgmt-Console)
Explanation: This console has been removed as it was no longer developed after Windows Server 2019. It's recommended to migrate from IIS 6.0 or earlier versions to the latest IIS version available in the most recent Windows Server release.
Feature: Wordpad
Explanation: WordPad has been removed from Windows Server 2025. For rich text documents (.doc, .rtf), use Microsoft Word, and for plain text documents (.txt), use Windows Notepad.
Feature: SMTP Server
Explanation: The SMTP Server feature has been removed from Windows Server 2025 with no direct replacement in the operating system.
Feature: Windows PowerShell 2.0 Engine
Explanation: The Windows PowerShell 2.0 Engine has been removed. Applications and components should now be migrated to PowerShell 5.0 or later.
Deprecated Services in Windows Server 2025
Feature: Computer Browser
Explanation: The Computer Browser driver and service are deprecated. This outdated and insecure protocol was first disabled by default in Windows 10 with the removal of SMB1. For more information, see MS-BRWS Common Internet File System.
Feature: NTLM
Explanation: All versions of NTLM, including LANMAN, NTLMv1, and NTLMv2, are deprecated and no longer under active development. While NTLM will continue to function, it is recommended to replace NTLM calls with Negotiate, which attempts Kerberos authentication first. For further details, refer to The evolution of Windows authentication.
Feature: Remote Mailslots
Explanation: Remote Mailslots are deprecated. This old and insecure IPC method, introduced in MS-DOS, was first disabled by default in Windows 11 Insider Preview Build. For more details, see About Mailslots and [MS-MAIL]: Remote Mailslot Protocol.
Feature: TLS 1.0 - TLS 1.1
Explanation: TLS versions 1.0 and 1.1 have been deprecated due to security concerns and are disabled by default as of the 2024 Windows Server Insiders Preview release. For more information, see TLS 1.0 and TLS 1.1 deprecation in Windows.
Feature: WebDAV Redirector service
Explanation: The WebDAV Redirector service is deprecated and is not installed by default in Windows Server. For more information, see WebDAV – Win32 apps.
Feature: Windows Management Instrumentation Command-line (WMIC)
Explanation: WMIC is disabled by default in new Windows Server installations and will be removed in a future release. Use PowerShell for WMI instead. For more information, see WMI command line (WMIC) utility deprecation: Next steps.
Feature: VBScript
Explanation: VBScript is deprecated and will be available as a feature on-demand before it is removed from future Windows releases.
Conclusion
Most of these changes should not significantly impact your environment. However, if your setup relies on legacy components such as NTLM, you should pay attention to the development plans and transition to Kerberos as soon as possible to address technical debt. Start identifying and managing this transition now.
If you're embarking on a Windows Server 2025 journey and want to learn how to integrate it with Azure Arc and cloud technology, you can begin your journey here.